Research
The Computational Dynamics Group (CODY) applies and develops theoretical and computational tools and methodologies in an interdisciplinary environment for understanding the behavior of nonlinear systems in different settings:
Topics
Biomathematics
Numerical and analytical study of mathematical models in Biomathematics.
- Mathematical neuroscience. Mathematical neuron models, bifurcation analysis, design of new computational tools in neuroscience, fast-slow systems, bursting-spiking transition, coupled neuron systems (CPGs), neuron networks.
- Non-linear cardiac dynamics. Mathematical myocyte models, bifurcation analysis, design of new computational tools in cardiac dynamics, cardiac arrhythmia.
-
Numerical detection of patterns in CPGs: Gait patterns in insect movement.
, , and . Communications in Nonlinear Science and Numerical Simulation 82 (2020) 105047. -
Bifurcations and slow-fast analysis in a cardiac cell model for investigation of early afterdepolarizations.
, , and . Mathematics 8 6 (2020) 880. -
Control strategies of 3-cell Central Pattern Generator via global
stimuli.
, and . Scientific reports 6 (2016) 23622.
Dynamical Systems
Development of new numerical methods for dynamical systems problems. Theoretical study of models.
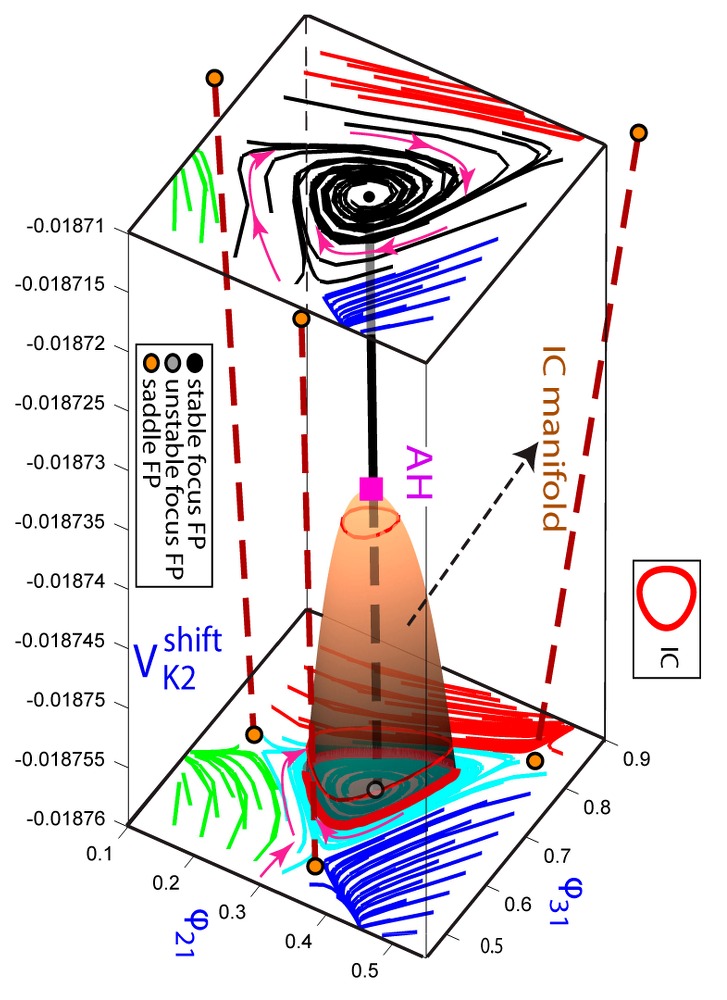
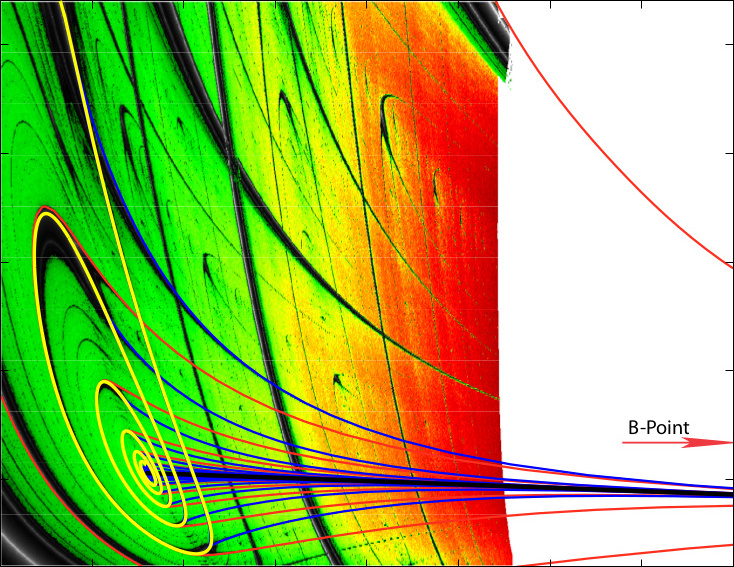
- Dissipative systems. Low dimensional systems, crossroad formation in parameter space, homoclinic codimension-2 bifurcations, hyperchaos, periodically forced systems.
- Computer Assisted Proofs. Rigorous proof of the existence of invariants.
- Computational tools. Perturbation theory, bifurcation analysis, parameter sweeping techniques, Lyapunov exponents, chaos indicators.
-
Spike-adding structure in fold/hom bursters.
, , and . Communications in Nonlinear Science and Numerical Simulation 83 (2020) 105100. -
Coexistence and dynamical connections between hyperchaos and chaos
in the 4D Rössler system: A computer-assisted proof.
, and . SIAM Journal on Applied Dynamical Systems 15 1 (2016) 356-390. -
Topological changes in periodicity hubs of dissipative systems.
, and . Physical Review Letters 108 21 (2012) 214102.
Numerical Analysis
Design and theoretical study of new methods in Numerical Analysis, focusing in applications to Dynamical Systems
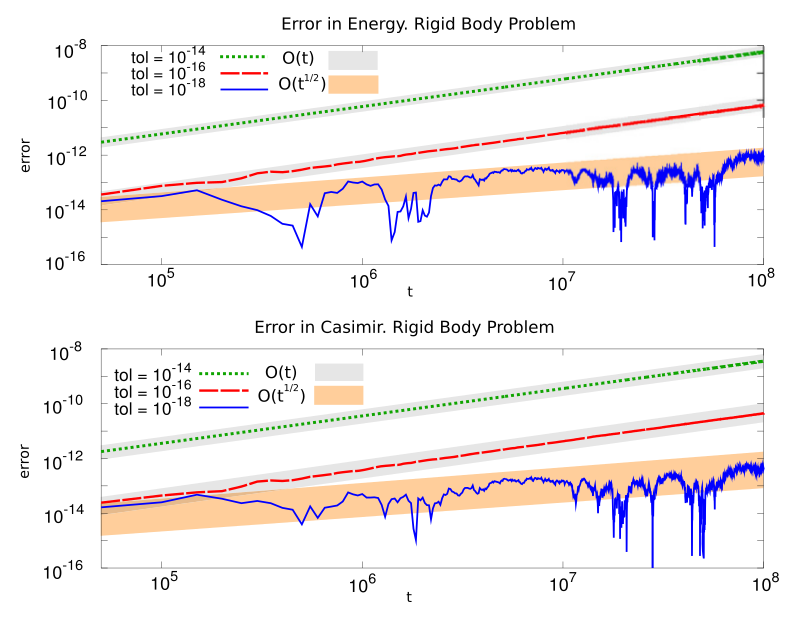
- ODE and DAE systems. New numerical methods for ODEs, Taylor Series method.
- Numerical linear algebra. Stability theory, evaluation of special functions, optimization algorithms, orthogonal polynomials and applications
- High-precision numerical analysis. High-precision numerical linear algebra, high-precision solution of ODEs, rigorous computing.
-
ORTHOPOLY: A library for accurate evaluation of series of classical orthogonal polynomials and their derivatives.
, , and . Computer Physics Communications 231 2 (2018) 146–162. -
A general condition number for polynomials
, and . SIAM Journal on Numerical Analysis 51 2 (2013) 1280-1294. -
Algorithm 924: Tides, a Taylor series integrator for differential
equations.
, , and . ACM Transactions on Mathematical Software 39 1 (2012) 5.
Full list of publications
Recent publications
- , , , , , and . Almost synchronization phenomena in the two and three coupled Brusselator systems , Physica D: Nonlinear Phenomena 472 (2025) 134457. doi 10.1016/j.physd.2024.134457
- , , , and . Coupling of neurons favors the bursting behavior and the predominance of the tripod gait, Chaos, Solitons & Fractals 184 (2024) 114928. doi 10.1016/j.chaos.2024.114928
- , , and . Dominant patterns in small directed bipartite networks: ubiquitous generalized tripod gait , Nonlinear Dynamics 112 (2024) 15549–15565. doi 10.1007/s11071-024-09830-2
- , and . Fast-slow analysis and bifurcations in the generation of the early afterdepolarization phenomenon in a realistic mathematical human ventricular myocyte model , Chaos: An Interdisciplinary Journal of Nonlinear Science 34 12 (2024).
- , , and . Full Lyapunov exponents spectrum with Deep Learning from single-variable time series , Physica D: Nonlinear Phenomena (2024) 134510.
- , and . Exploring the geometry of the bifurcation sets in parameter space , Scientific Reports 14 1 (2024) 10900.
- , , , and . Understanding the role of B cells in CAR T-cell therapy in leukemia through a mathematical model, Chaos: An Interdisciplinary Journal of Nonlinear Science 34 8 (2024) 083142. doi 10.1063/5.0206341
- , , , and . Synaptic dependence of dynamic regimes when coupling neural populations , Physical Review E 109 1 (2024) 6337.
- , , , , , , and . Connecting chaotic regions in the Coupled Brusselator System, Chaos, Solitons & Fractals 169 (2023) 113240. doi 10.1016/j.chaos.2023.113240
- and . Authoritarianism versus participation in innovation decisions, Technovation 124 (2023) 102741. doi 10.1016/j.technovation.2023.102741